Page snapshot: Utah State Geologic Map; Fossil; Rock; Mineral; Gem; Highest and Lowest Elevations; Places to Visit; and Additional Resources.
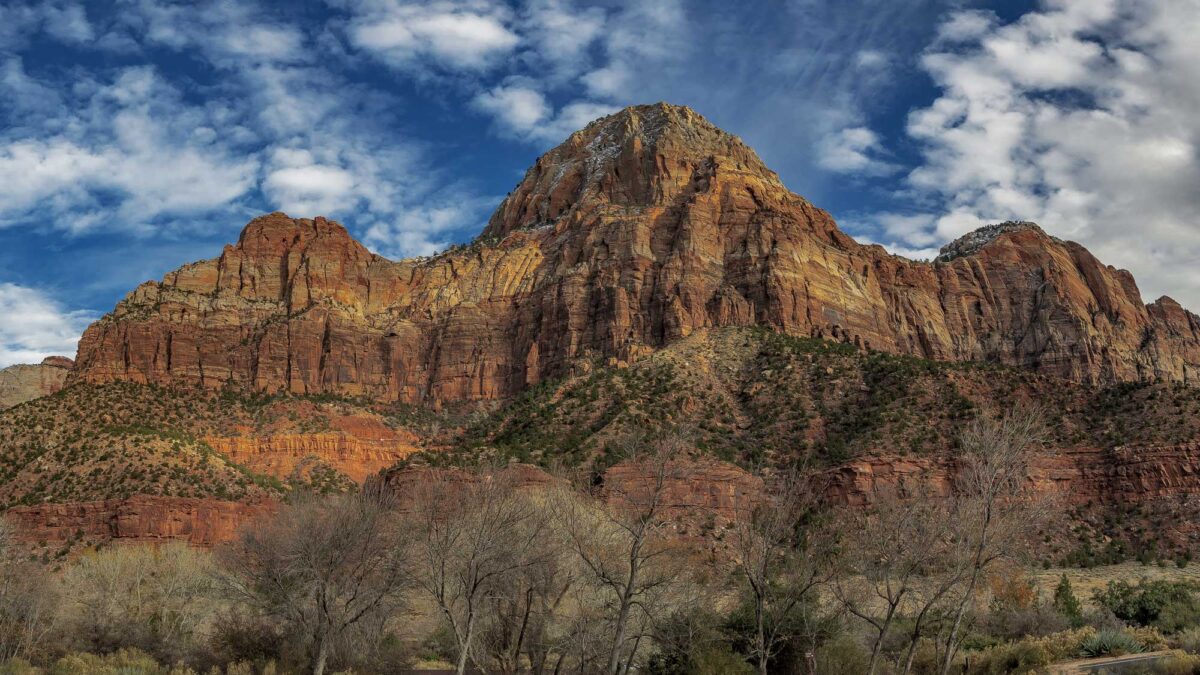
Image above: Rock exposures at Zion National Park in Utah. Photograph by Ken Lane (Flickr; Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.0 Generic license; image cropped and resized).
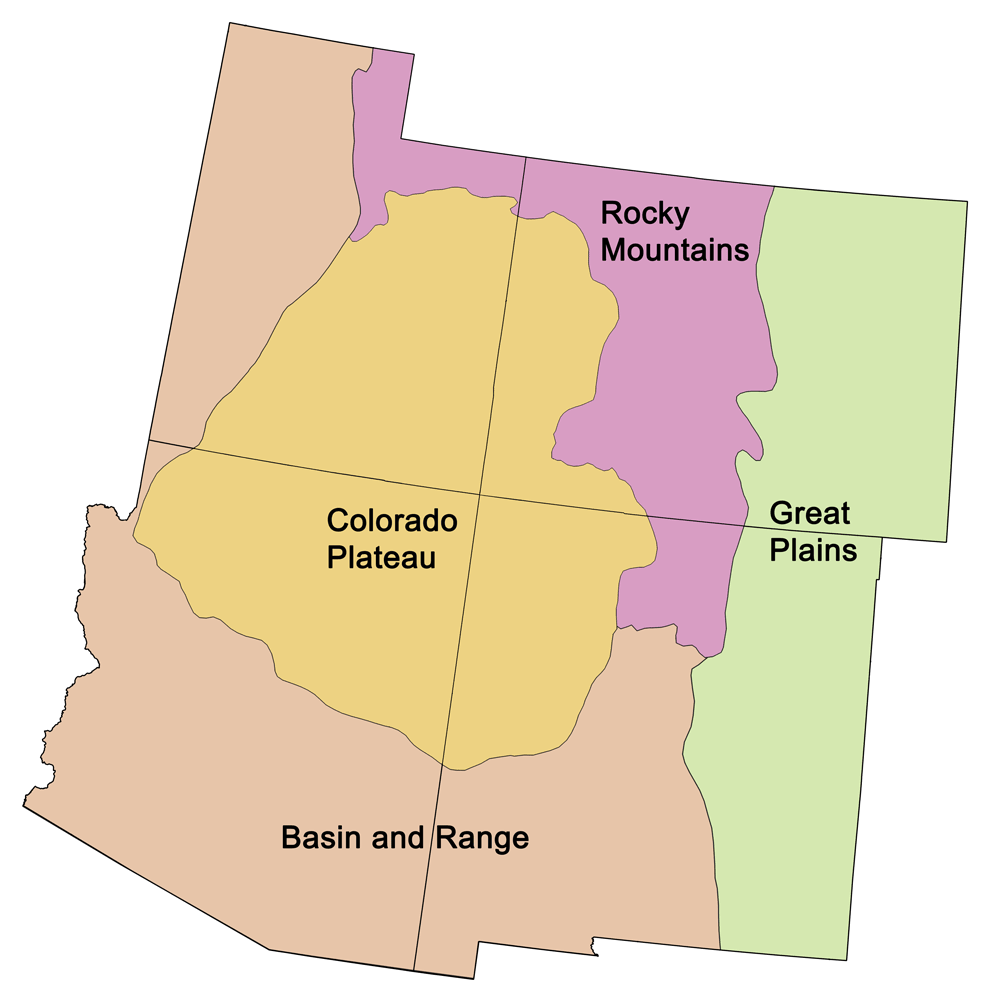
Geologic Maps of Utah
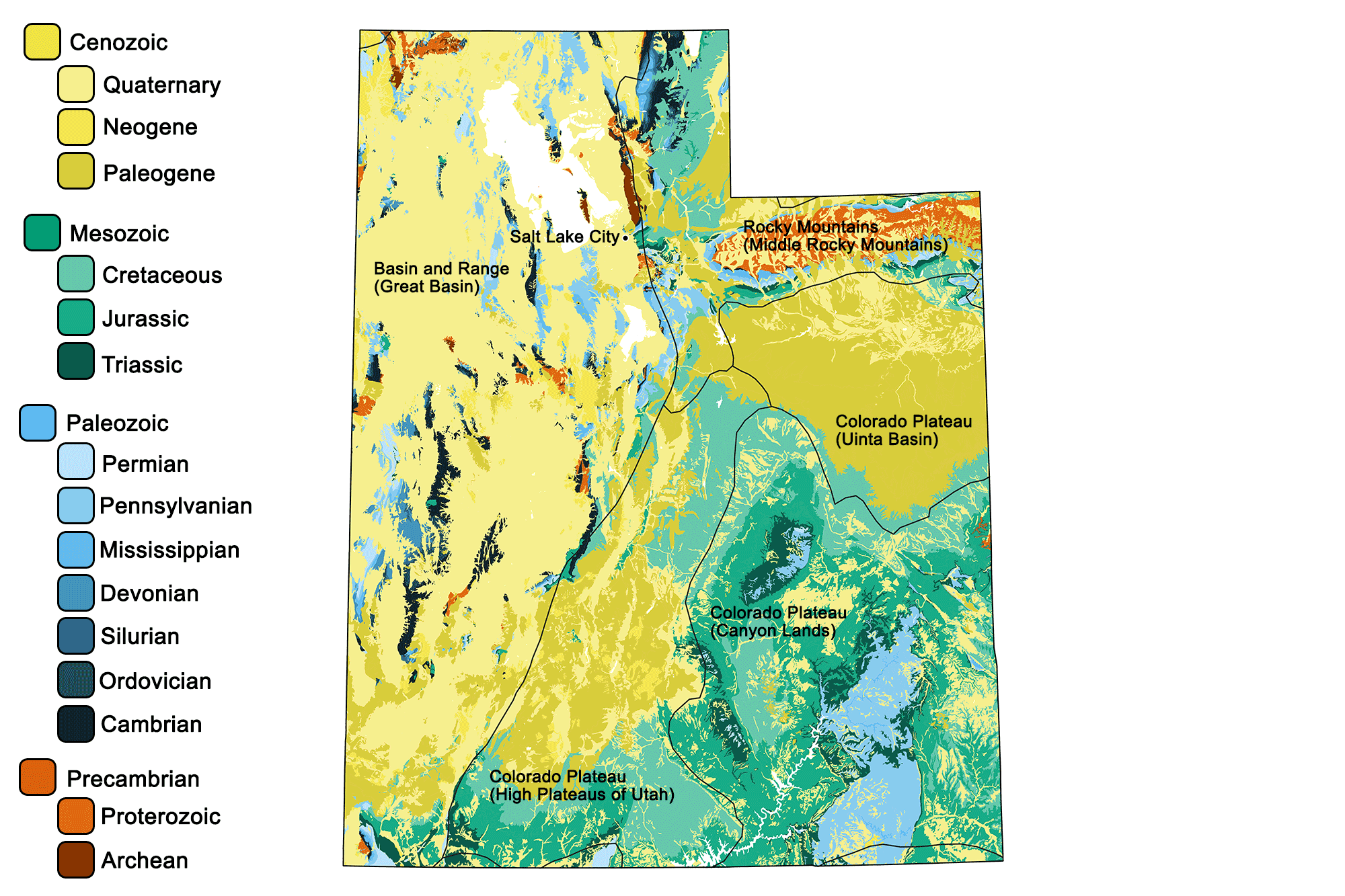
Geologic map of Utah showing maximum ages of mappable units. Image by Jonathan R. Hendricks for the Earth@Home project developed using QGIS and USGS data (public domain) from Fenneman and Johnson (1946) and Horton et al. (2017).
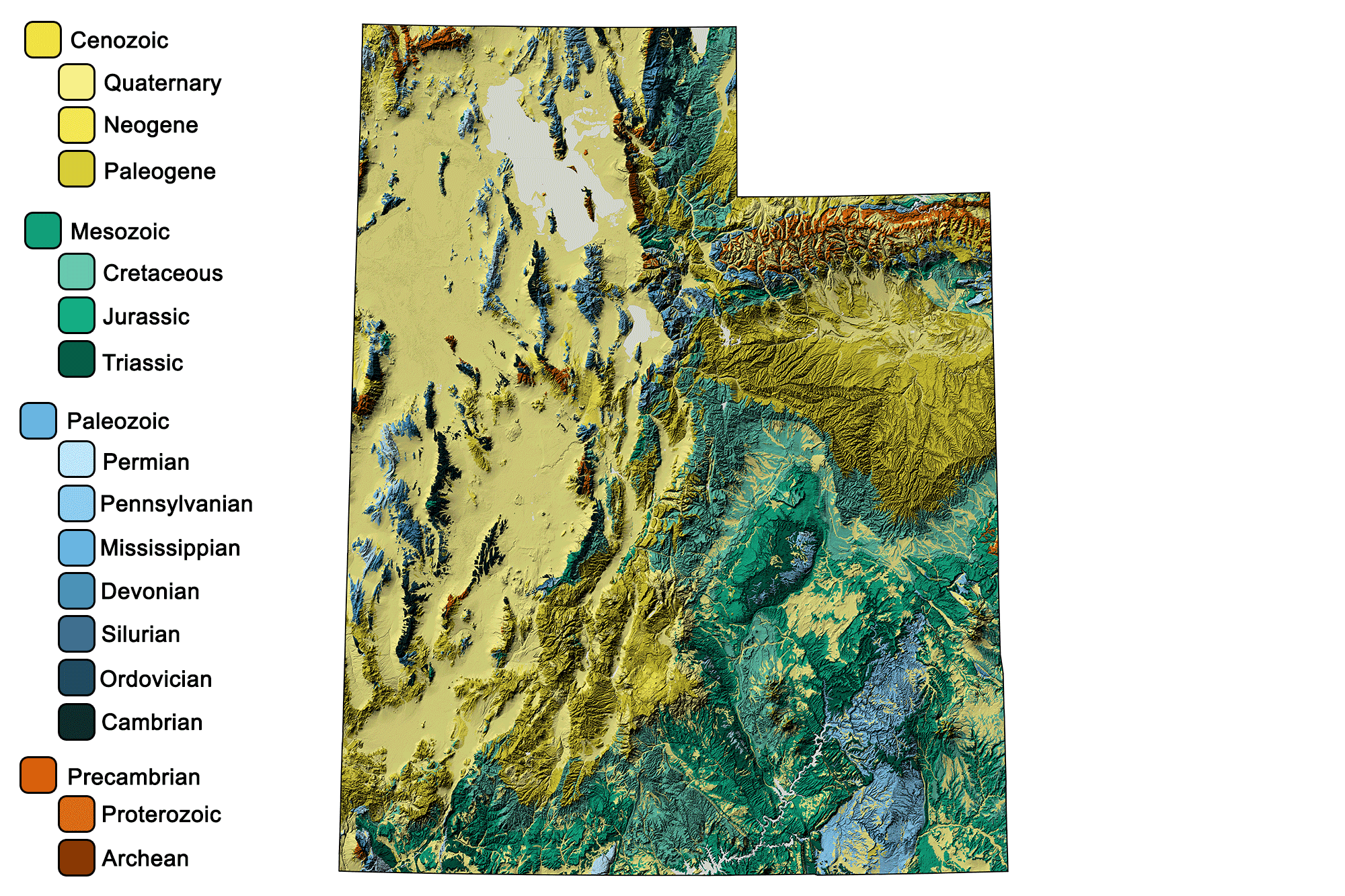
Geologic and topographic map of Utah. Geologic data from Horton et al. (2017) using the maximum age values for each mapped unit. Topographic data are derived from the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM GL3) Global 90m (SRTM_GL3) (Farr, T. G., and M. Kobrick, 2000, Shuttle Radar Topography Mission produces a wealth of data. Eos Trans. AGU, 81:583-583).
Utah State Fossil: Allosaurus fragilis
The state fossil of Utah is the carnivorous Jurassic dinosaur Allosaurus fragilis.
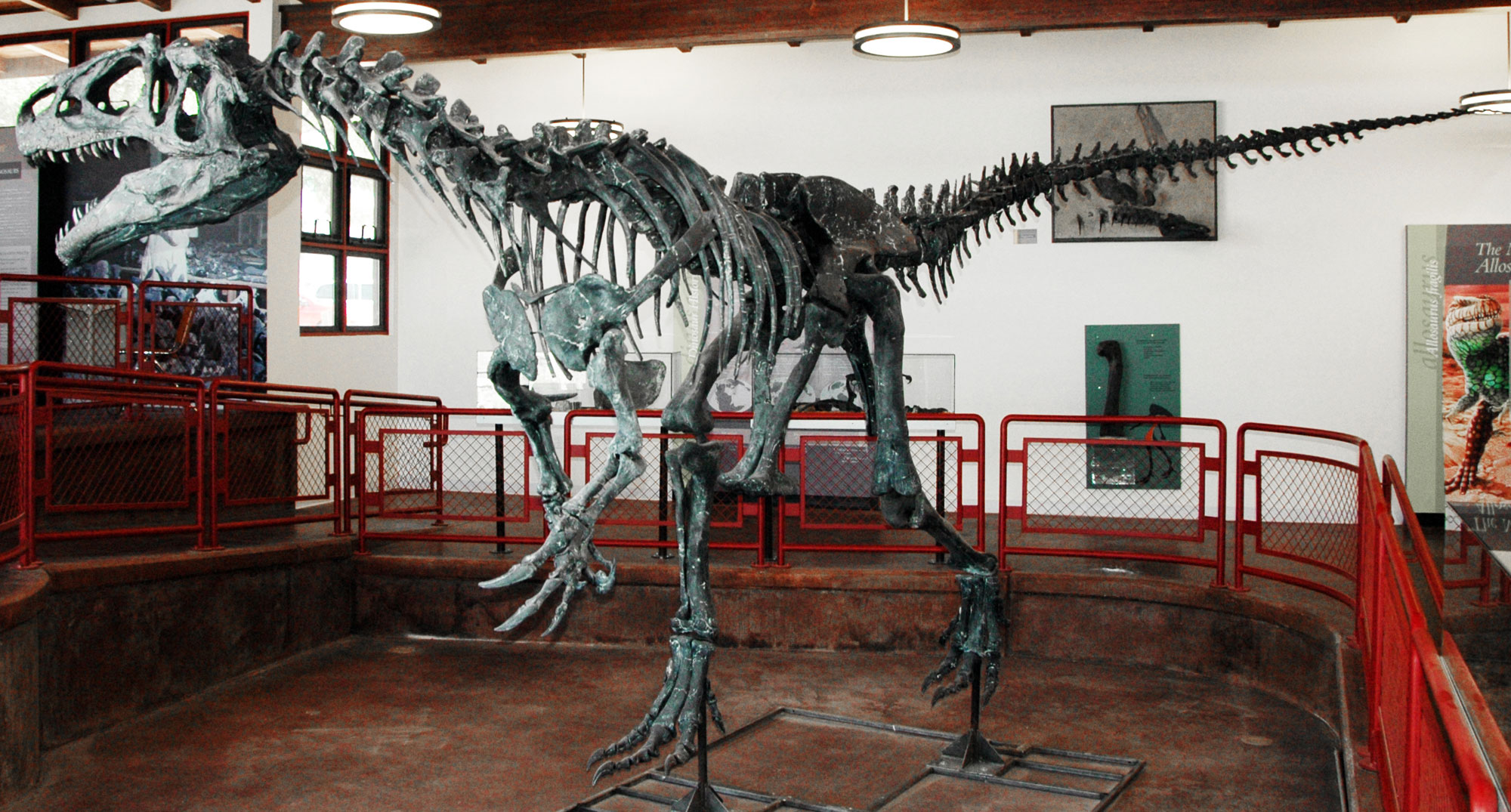

Allosaurus fragilis on display at the Cleveland-Lloyd Dinosaur Quarry, Utah. Photo by James St. John (flickr, Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic license, image resized).
Utah State Rock: Coal
Coal is found in 17 of Utah’s 29 counties, but coal mining is primarily concentrated in Emery and Carbon counties, where coals formed in the Uinta Basin. Most coal mined in Utah is bituminous.
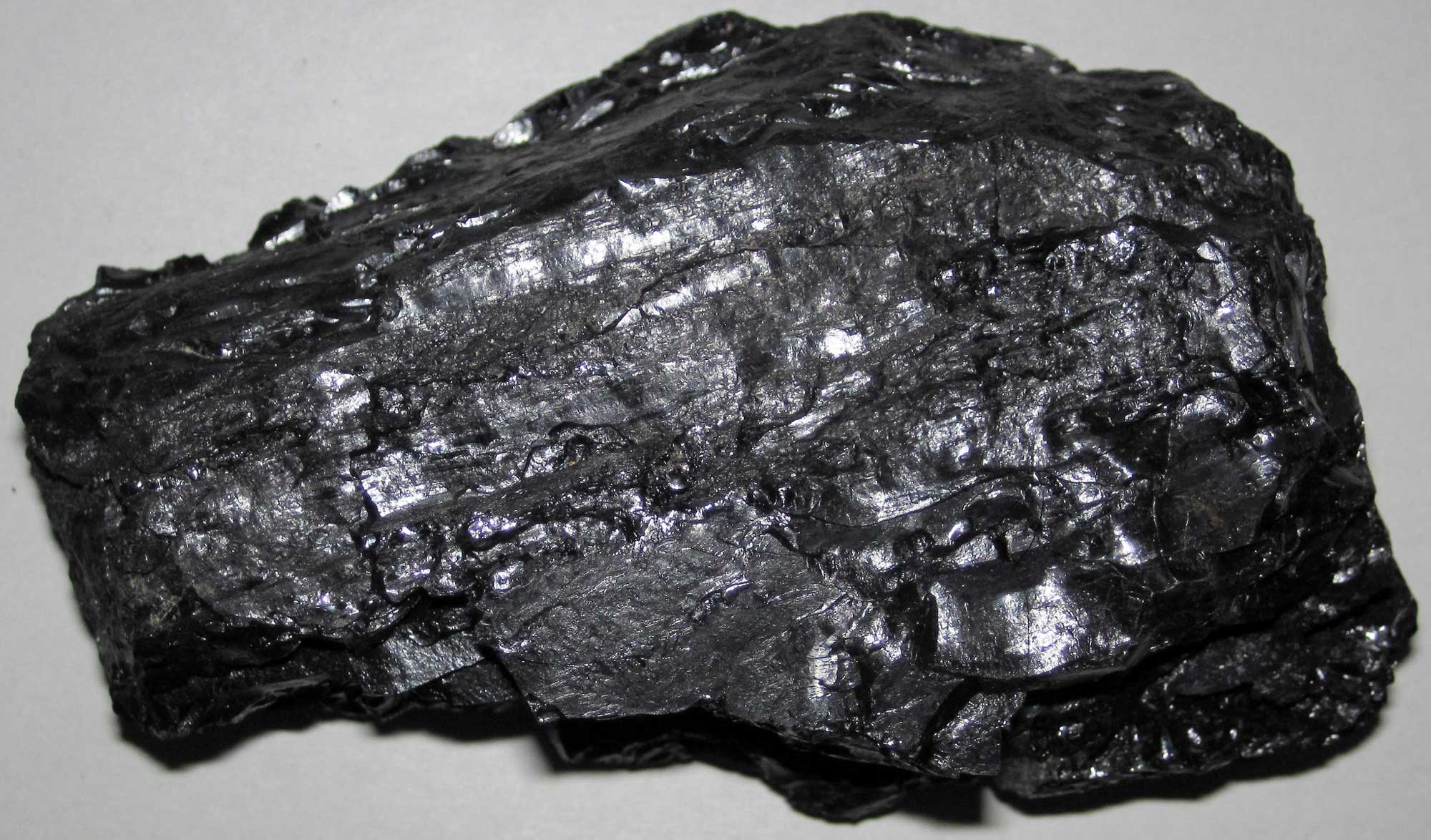

Bituminous coal from Emery County, Utah. Photograph by James St. John (Flickr; Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic license; image resized).
Utah State Mineral: Copper
The Kennecott’s Bingham Canyon mine in the Oquirrh Mountains is the world’s largest open-pit copper mine. Copper is a versatile metal widely valued for its capacity to conduct heat and electricity, and is used in electronics, transportation, plumbing, and alloys, among many other areas.
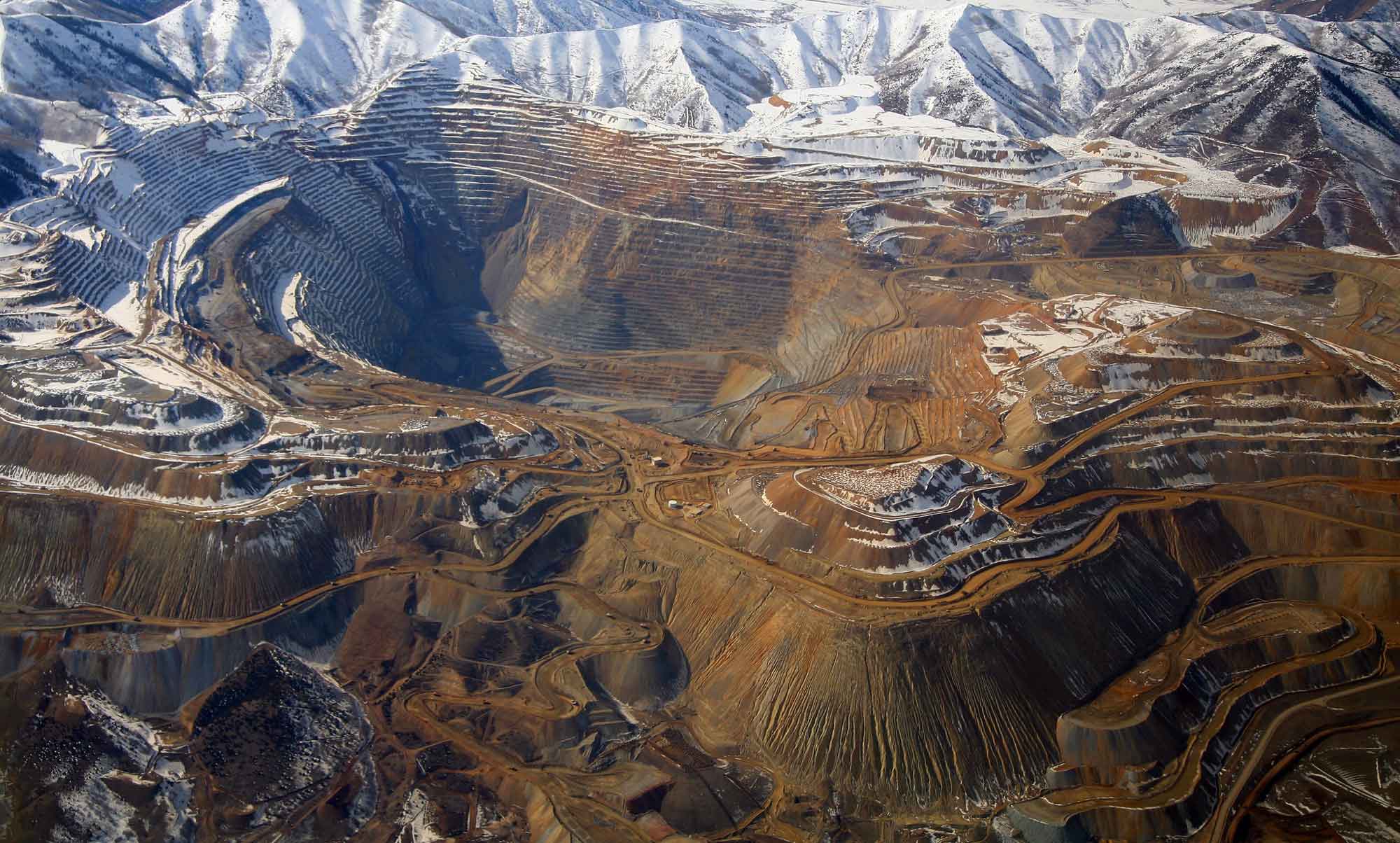

Bingham Canyon Cooper Mine in Utah. Photograph by Doc Searls (Flickr; Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic license; image resized).
Utah State Gem: Topaz
Topaz is a hard, semiprecious gem that is found in Beaver, Juab, and Tooele counties in Utah. At Topaz Mountain, which is in the Thomas Mountain Range in Juab County, topaz and other minerals such as beryl and opal are found in relatively high abundance in the cavities of Neogene-aged rhyolites.
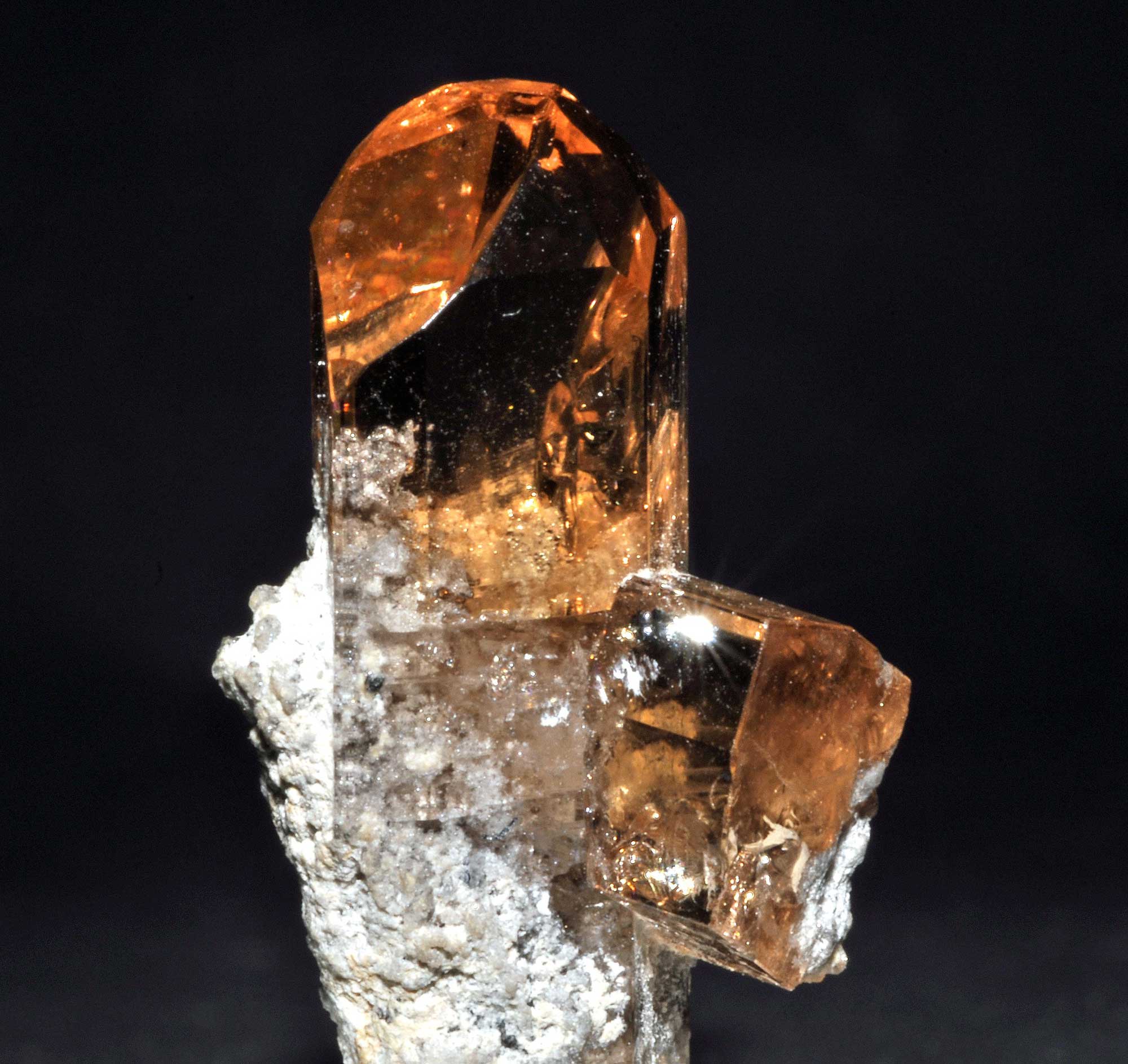

Sample of Topaz from Topaz Mountain, Juab County, Utah. Photograph by Géry Parent (Wikimedia Commons; public domain).
Utah's Highest and Lowest Elevations
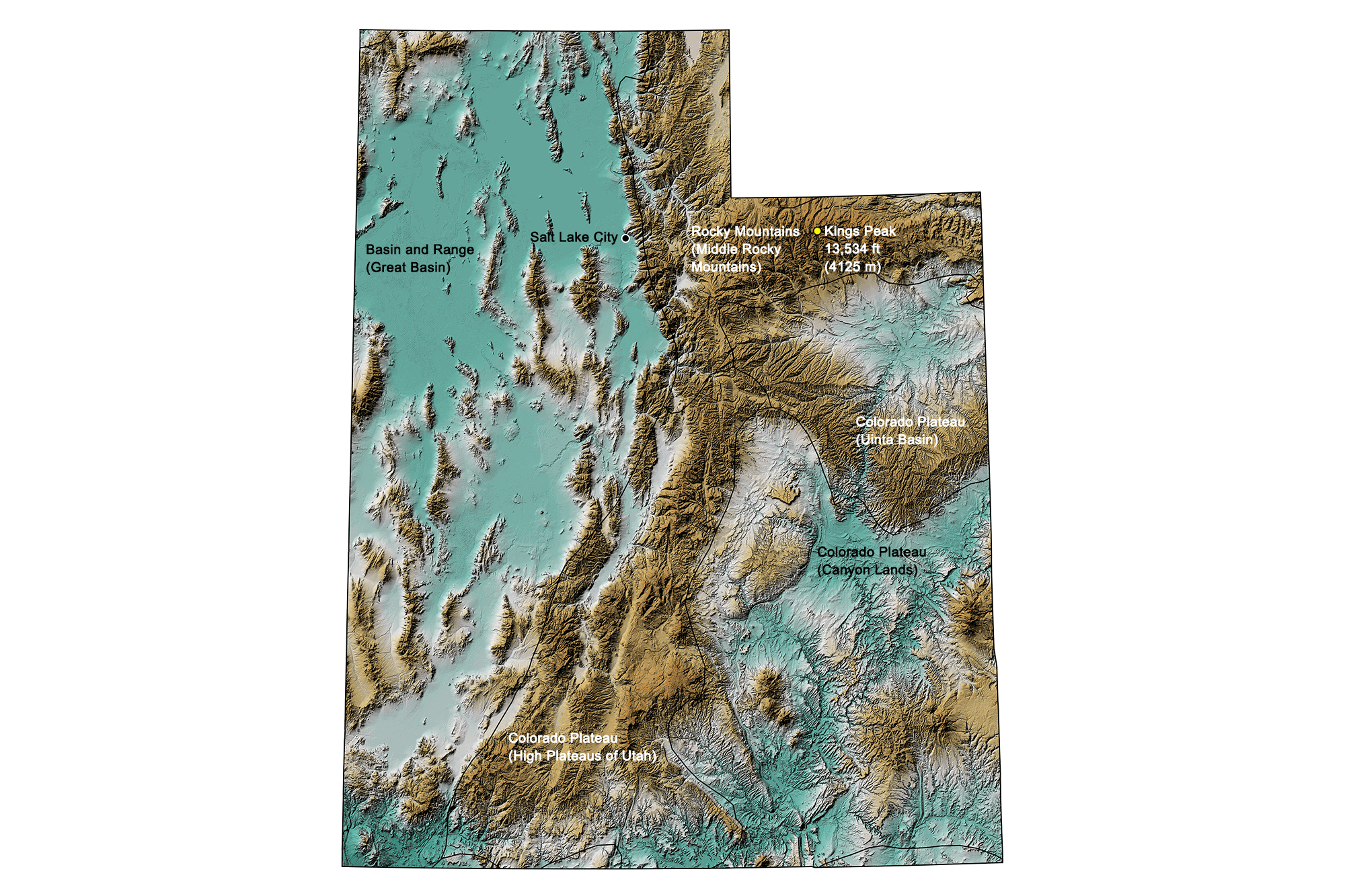
Topographic map of Utah with physiographic regions and point of highest elevation identified. Topographic data are derived from the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM GL3) Global 90m (SRTM_GL3) (Farr, T. G., and M. Kobrick, 2000, Shuttle Radar Topography Mission produces a wealth of data. Eos Trans. AGU, 81:583-583).
Highest Elevation: Kings Peak
At 4125 meters (13,534 feet), Kings Peak is Utah's highest point, located in the Uinta Mountains of north-central Duchesne County. The peak is regarded as the hardest state high point to climb without special rock climbing skills or a guide; the easiest trail to the summit requires a 47-kilometer (29-mile) round-trip hike.
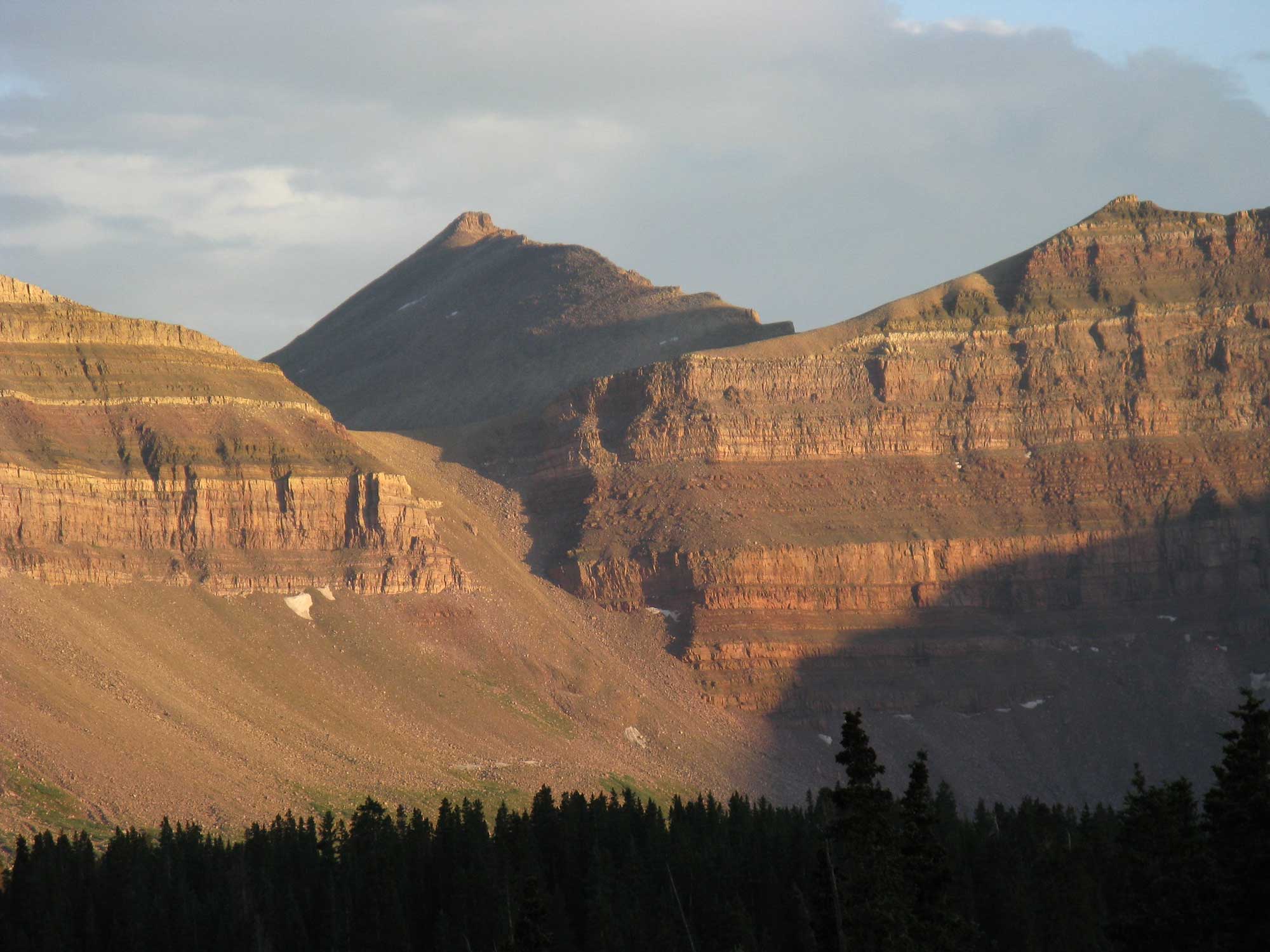

Kings Peak, Utah. Photograph by Casey Goodlett (Flickr; Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 2.0 Generic license; image resized).
Lowest Elevation: Beaver Dam Wash
Beaver Dam Wash, at the Utah-Arizona state line in Washington County, is the lowest point in the state at 664 meters (2178 feet) above sea level.
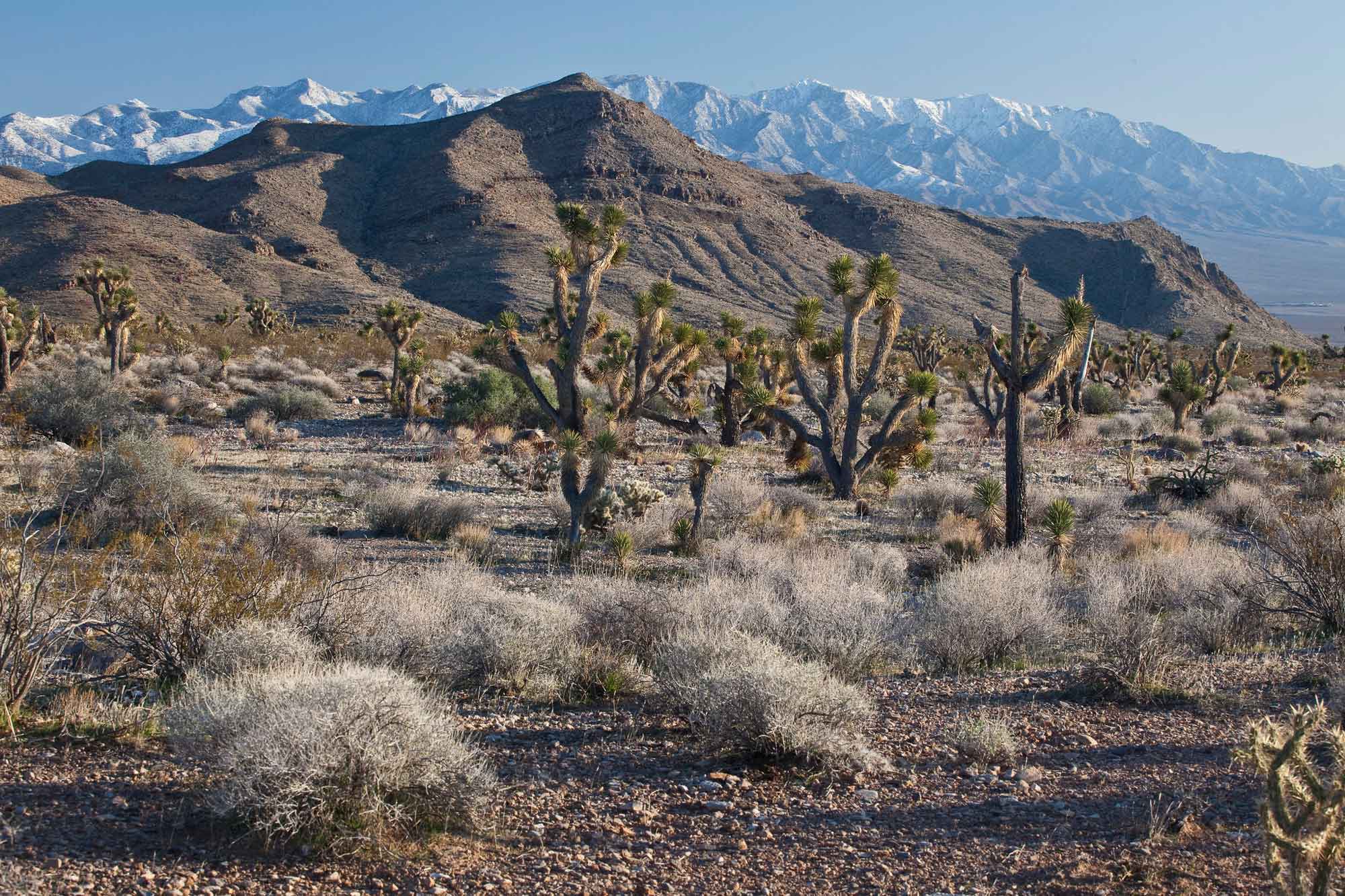

Beaver Dam Wash National Conservation Area, Utah. Photograph by Bureau of Land Management (Flickr; Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic license; image resized).
Places to Visit
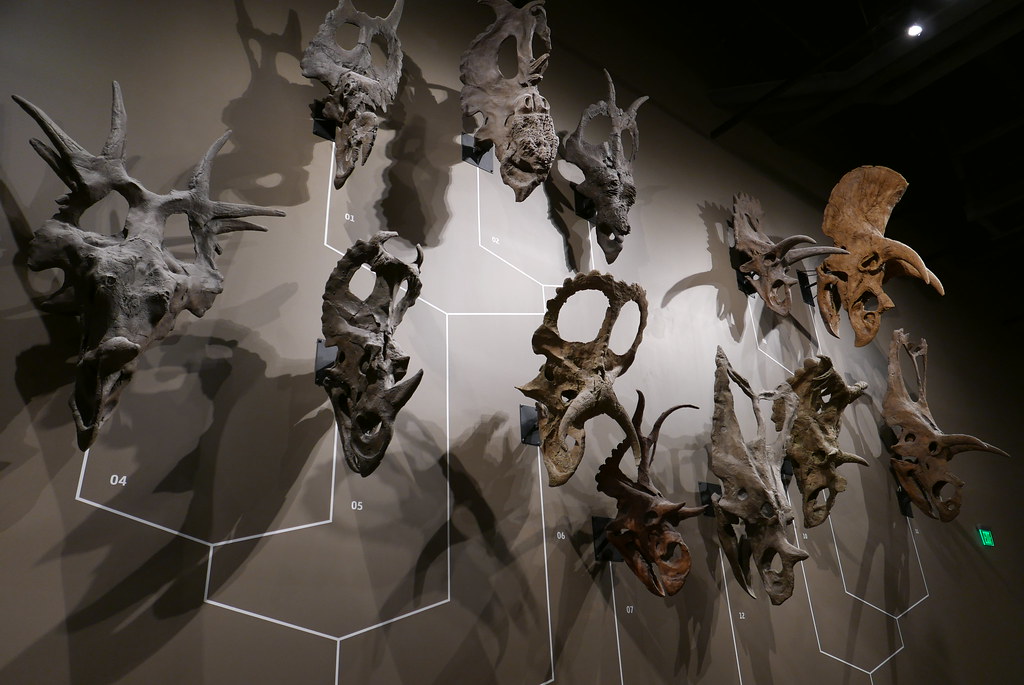

Ceratopsian dinosaur skulls on display at the Natural History Museum of Utah. Photograph by "rameylady" (Flickr; Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 2.0 Generic license).
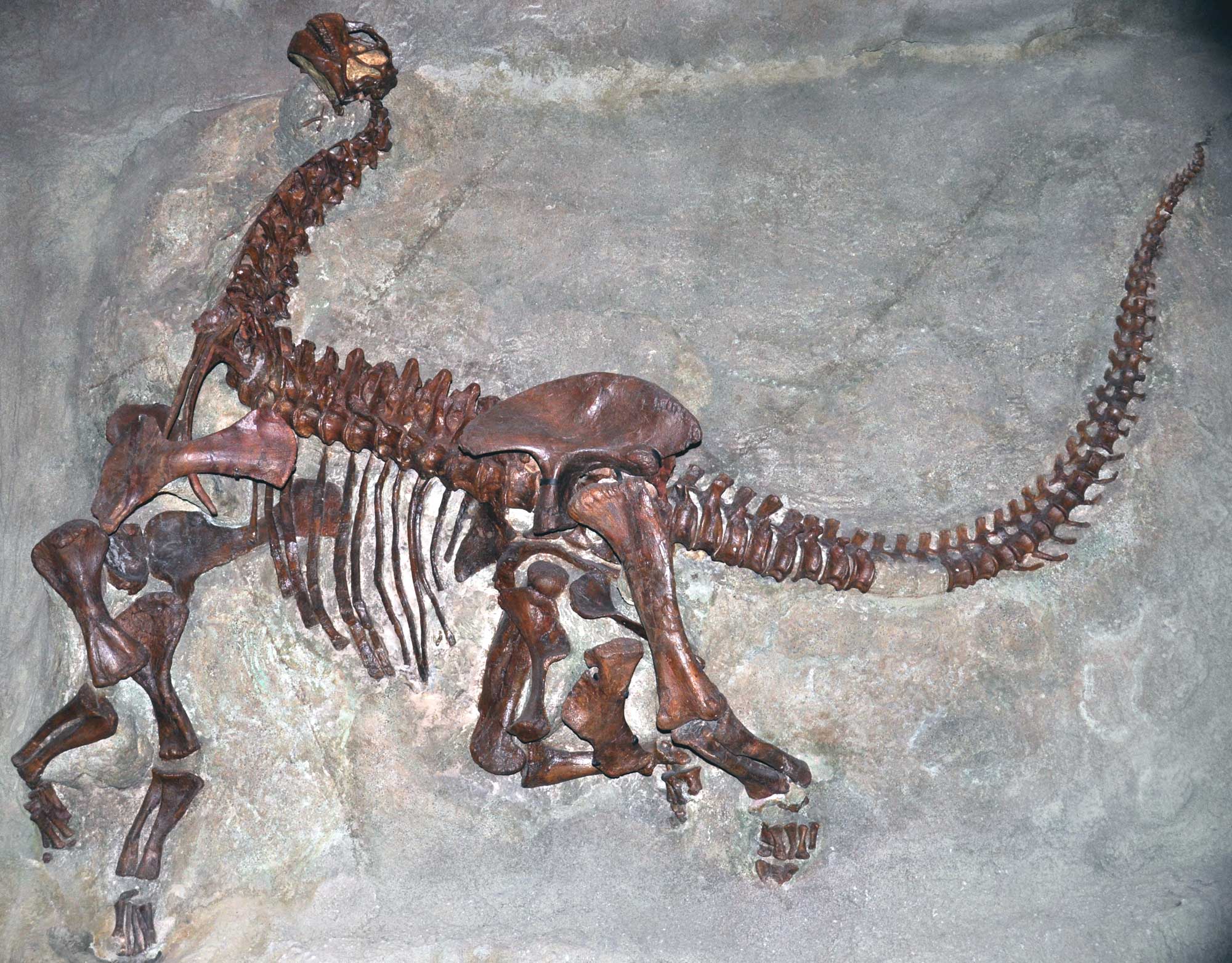

Skeleton of a juvenile Camarosaurs lentus, a type of sauropod, from the Carnegie Quarry, Jurassic Morrison Formation, Dinosaur National Monument, Utah and Colorado. Photo by James St. John (flickr, Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic license, image cropped and resized).