Chapter Contents
- Why We Need to Adapt and Build Resilience
- The Costs and Benefits of Adaptation
- Types of Adaptation Strategies
- Adaptation to Different Climate Hazards
- Climate Justice and Equity
- Summary and Additional Resources
- Activities for Climate Change Adaptation Chapter
Image above: Rain garden in the Allen Centennial Gardens on the campus of the University of Wisconsin-Madison. Photo by James Steakley via Wikimedia Commons (CC BY-SA 4.0). Image cropped by PRI.
The table below lists examples of different types of adaptation strategies. It does not address every possible hazard associated with climate change and is not meant to be comprehensive. Rather, it is meant to give examples of a range of strategies which communities, governments, and businesses can use to adapt to climate change. Since climate change impacts vary geographically and in different sectors, different adaptation strategies will apply in different regions and communities. Some strategies are “win-win” or “no-regrets,” that is, they have benefits beyond adapting to climate change and should probably be done anyway. Others can be seen as more drastic.
Adaptation Strategy: Relocate and Retreat
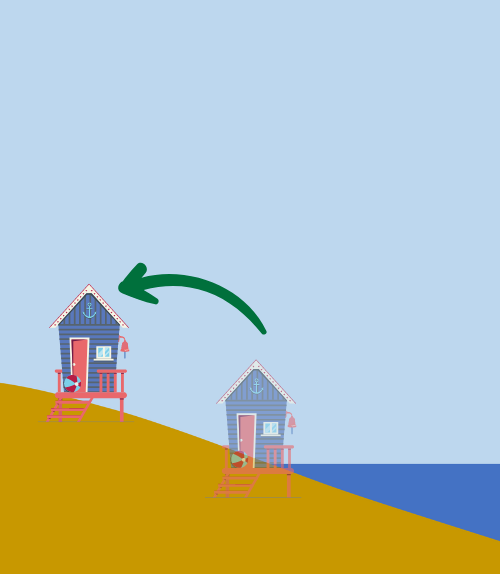
Beach house relocated to higher ground. Image created by Ingrid Zabel for PRI's Earth@Home project (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license) with images from Canva.
Sea Level Rise
- Climate Hazard: Coastal flooding, permanent inundation of coastal areas
- Adaptation Strategy: Relocate homes and infrastructure to higher elevations
Heavy Downpours
- Climate Hazard: Increased flood risk
- Adaptation Strategy: Implement phased withdrawal of infrastructure from flood-prone areas
Adaptation Strategy: Make Changes in Built Infrastructure
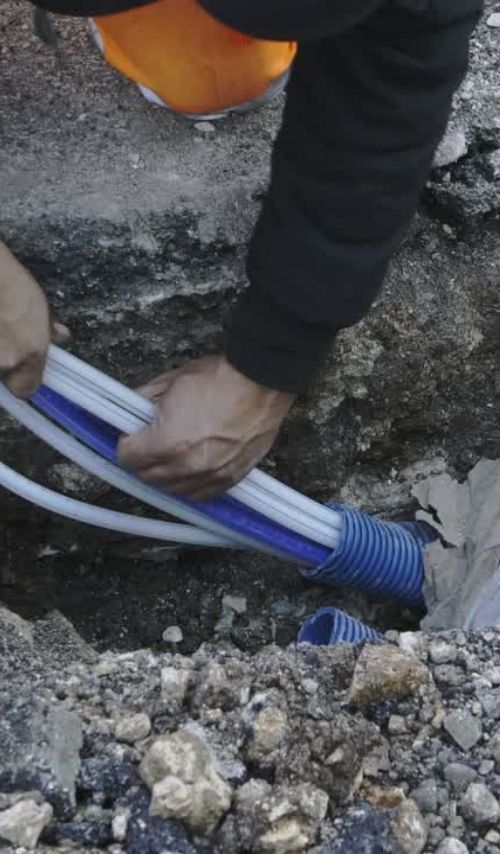

Worker installing underground fiber optic cables. Photo: Canva
Extreme Storms
- Climate Hazard: Damage to power and communication lines
- Adaptation Strategy: Relocate lines underground where possible
Extreme Heat
- Climate Hazard: Decreasing dairy productivity due to heat stress in cows
- Adaptation Strategy: Alter livestock barns to increase cooling capacity
Sea Level Rise
- Climate Hazard: Coastal flooding and property damage
- Adaptation Strategy: Build structures to attenuate waves and storm surges
Adaptation Strategy: Renew and Conserve Natural Systems
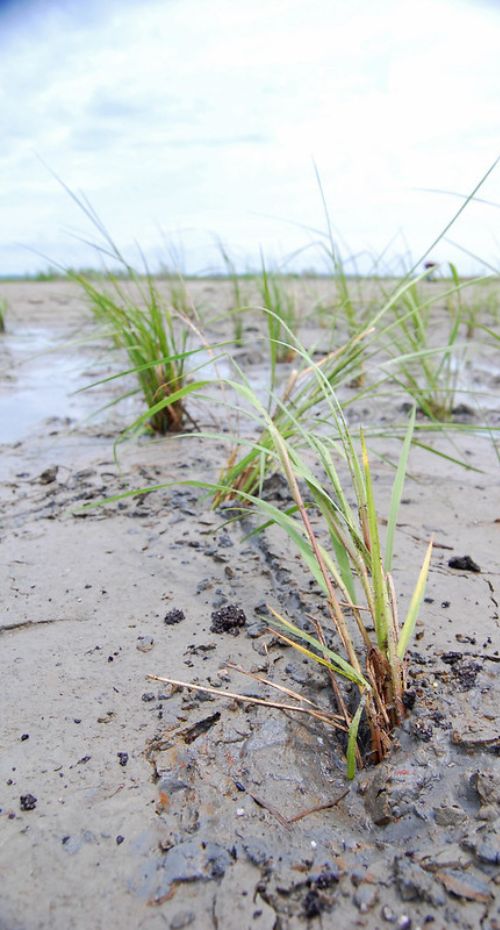

Sea Level Rise
- Climate Hazard: Coastal erosion and loss of wetlands
- Adaptation Strategy: Renourish beaches, plant coastal vegetation, and restore wetlands
Heavy Downpours
- Climate Hazard: Riverbank erosion and river flooding
- Adaptation Strategy: Stabilize riverbanks by planting deep-rooted, native
plants
Temperature Change
- Climate Hazard: Shifts in range of animal species
- Adaptation Strategy: Maintain habitat connectivity and migration corridors
Adaptation Strategy: Make Land Use Changes
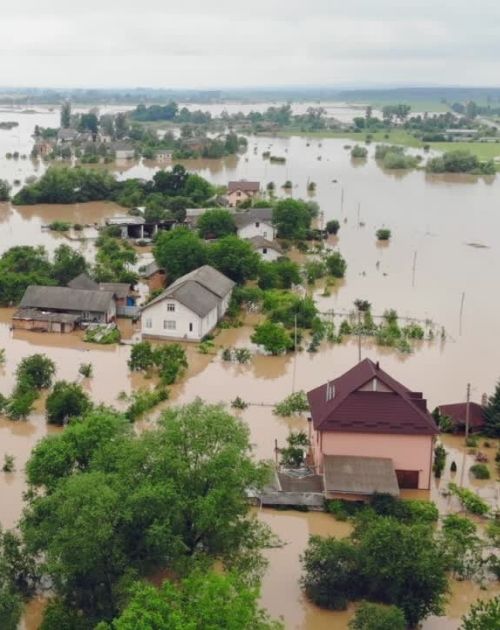

Flooded buildings and land. Photo: Canva
Heavy Downpours
- Climate Hazard: Increased flood risk and flood damage
- Adaptation Strategy: Encourage people to move out of flood-prone areas by buying out land or perform land swaps. In cities, soak up stormwater by increasing land area covered by gardens and bioswales.
Sea Level Rise
- Climate Hazard: Permanent inundation of coastal land
- Adaptation Strategy: Build up portions of low-lying cities
Adaptation Strategy: Modify Management and Operations

Extreme Heat
- Climate Hazard: Heat-related illness and death
- Adaptation Strategy: Increase power supply for air conditioning and provide cooling centers for vulnerable populations
Extreme Storms
- Climate Hazard: Reduced bridge and roadway safety
- Adaptation Strategy: Plan to reduce or suspend traffic during extreme storms
Temperature Change
- Climate Hazard: Changing growing season and crop productivity
- Adaptation Strategy: Alter planting cycles, crop varieties, and crop type
Adaptation Strategy: Diversify
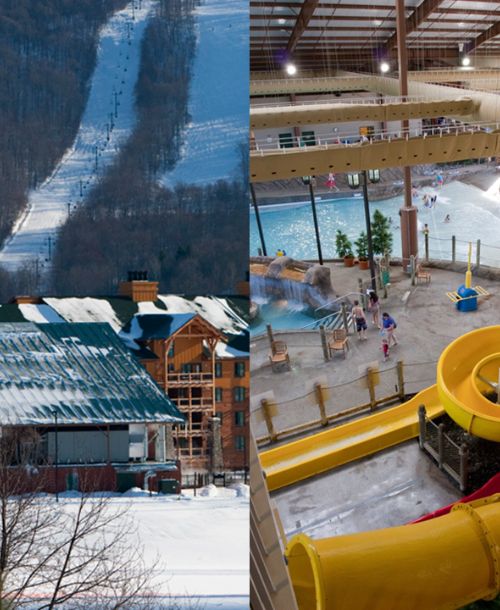

Reduced Snowfall
- Climate Hazard: Loss of wintertime tourism (skiing, snowmobiling)
- Adaptation Strategy: Shift and innovate other recreational and tourist activites
Temperature Change
- Climate Hazard: Reduced crop productivity at higher temperatures
- Adaptation Strategy: Develop new crop types and farming methods
Adaptation Strategy: Social Innovation
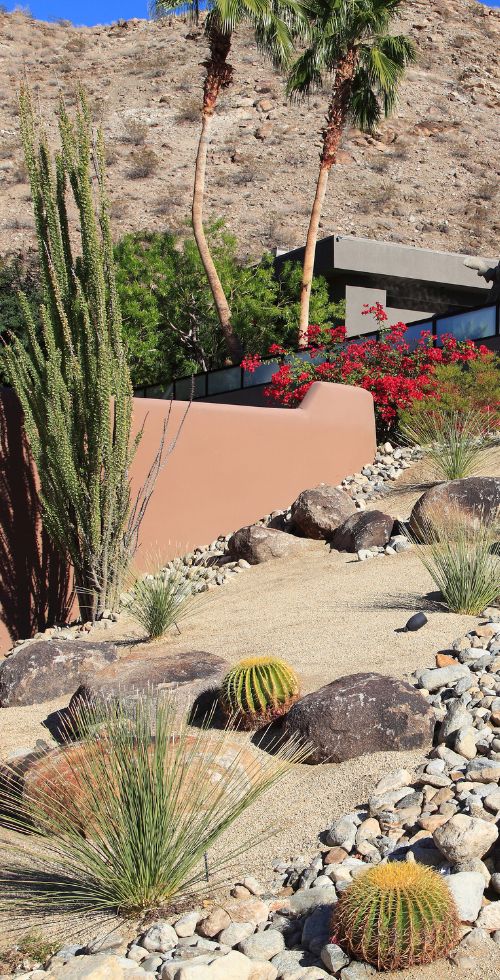

A garden for an arid environment. Photo: Canva
Reduced Snowpack
- Climate Hazard: Reduced snowpack runoff and water supply
- Adaptation Strategy: Encourage landscaping and gardening practices that
use drought-resistant plants and eliminate need for irrigation
Extreme Heat
- Climate Hazard: Heat-related illness and death
- Adaptation Strategy: Foster community networks that find and help at-risk
populations
Drought
- Climate Hazard: Stress on water supply
- Adaptation Strategy: Influence consumer water conservation behavior with
the use of smart meters and pricing
Adaptation Strategy: Risk Management
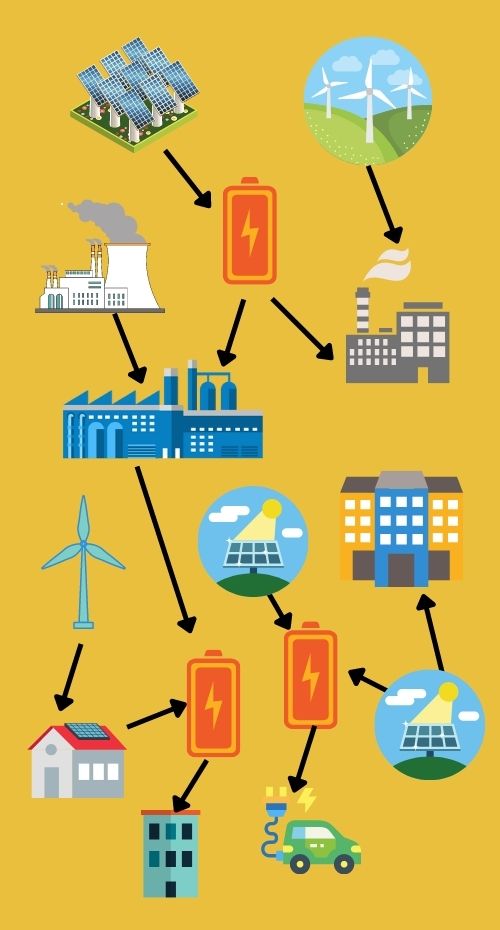
Diagram of distributed power generation. Image created by Ingrid Zabel for PRI's Earth@Home project (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license) with images from Canva
Extreme Weather
- Climate Hazard: Energy supply disruptions
- Adaptation Strategy: Increase distributed electricity generation (electricity from multiple, decentralized sources)
Extreme Storms
- Climate Hazard: Damage to transportation systems and other infrastructure
- Adaptation Strategy: Create mutual insurance pools to share risks
Drought
- Climate Hazard: Crop damage and failure
- Adaptation Strategy: Implement drought early warning systems to help growers plan, prepare, and respond
Adaptation Strategy: Policy Changes

Image created by Ingrid Zabel for PRI's Earth@Home project (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license) with images from Canva
Extreme Coastal Storms
- Climate Hazard: Damages to coastal property
- Adaptation Strategy: Update building codes to promote storm-resistant
structures
Sea Level Rise
- Climate Hazard: Loss of coastal wetland habitat
- Adaptation Strategy: Protect coastal wetlands with rolling easements
(recognize nature’s right-of-way to advance inland as sea level rises)
Drought
- Climate Hazard: Lack of water for hydropower plants
- Adaptation Strategy: Adjust reservoir release policies to ensure sufficient
summer hydropower capacity



