Contents
Topics covered on this page: Overview; Weathering; Erosion and deposition; Topography and rock structure; Summary
Credits: Most of the text of this page is derived from "Topography of the Southeastern US" by Michael A. Gibson and Andrielle Swaby, chapter 4 in The Teacher-Friendly Guide to the Earth Science of the SoutheasternU.S., 2nd ed., edited by Andrielle N. Swaby, Mark D. Lucas, and Robert M. Ross (published in 2016 by the Paleontological Research Institution; currently out of print). The book was adapted for the web by Elizabeth J. Hermsen and Jonathan R. Hendricks in 2021–2022. Changes include formatting and revisions to the text and images. Credits for individual images are given in figure captions.
Updates: Page last updated March 7, 2024.
Image above: A valley in the Great Smoky Mountains. Photograph by Wilfred Hdez (Flickr; Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic license; cropped and resized from original.
Overview
Does your region have rolling hills? Mountainous areas? Flat land where you never have to bike up a hill? The answers to these questions can help others understand the basic topography of your region. The term topography is used to describe the changes in elevation over a particular area and is, generally speaking, the result of two processes: deposition and erosion.
These two processes can occur over an enormous range of timescales. For example, a flash flood can erode away tons of rock in a matter of hours, yet which rock is broken down and which remains can depend on how it was formed hundreds of millions of years ago. Topography is often intimately tied to weathering and erosion, as well as to the type and structure of the underlying bedrock, but it is also a story of plate tectonics, volcanoes, folding, faulting, uplift, and mountain building.
Weathering
Weathering includes both the mechanical and chemical processes that break down a rock. There are two types of weathering: physical and chemical.
Physical weathering
Physical weathering describes the physical or mechanical breakdown of a rock, during which the rock is broken into smaller pieces but no chemical changes take place. Wind, water, temperature, and pressure are the main media by which physical weathering and erosion occur. Streams are constantly eroding their way down through bedrock to sea level, creating valleys in the process. Given sufficient time, streams can cut deeply and develop wide flat floodplains on valley floors. Streams, oceans, and ice also deposit the material they erode, creating new topographical features elsewhere. The pounding action of ocean waves on a coastline contributes to the erosion of coastal rocks and sediments, while the emptying of a river can lead to the formation of a delta.
Pressure release can cause rocks to crack. Growing plant roots can exert many pounds per square inch of pressure on rocks—think of tree roots uplifting and cracking a sidewalk. Additionally, since rocks buried miles beneath the surface are under considerable pressure, if those rocks become exposed at the Earth's surface (where the rock is under less pressure), the rock may expand and crack in a process called exfoliation.
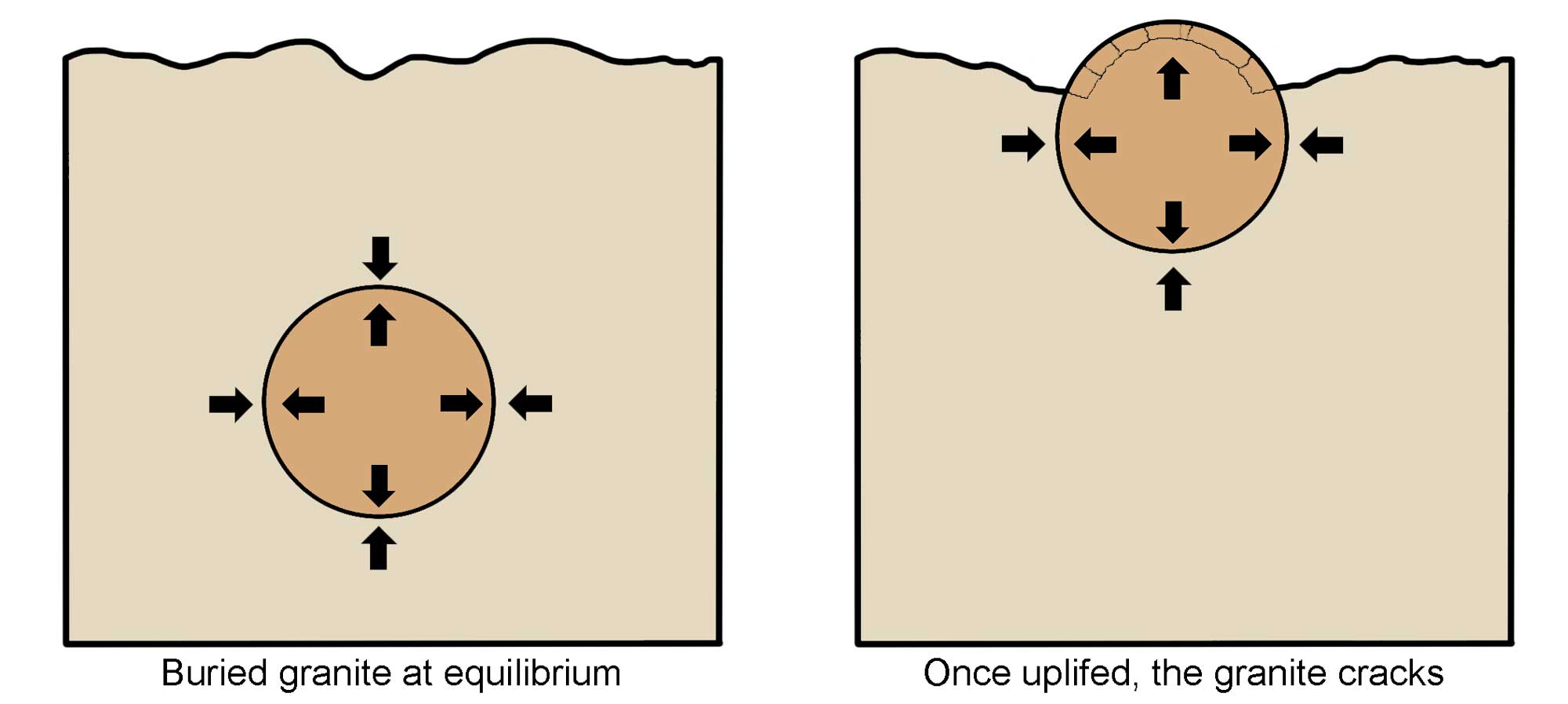
Diagram showing how the process of exfoliation works as a result of uplift and release of pressure. Image modified from original by Wendy Van Norden for the Earth@Home project.
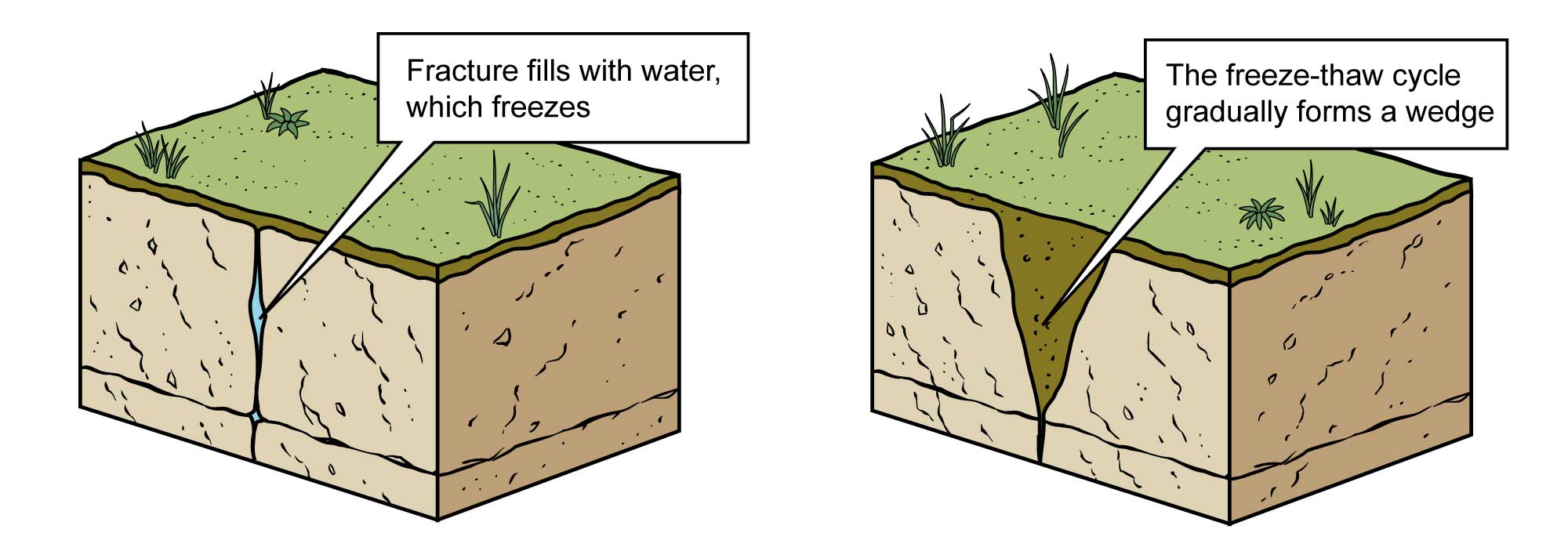
Physical weathering from a freeze-thaw cycle. Image modified from original by Jim Houghton for the Earth@Home project.
Chemical weathering
Working in conjunction with physical (mechanical) weathering, chemical weathering also helps to break down rocks through changes in the chemical composition of their constituent minerals.
Some minerals contained in igneous and metamorphic rocks that are formed at high temperatures and pressures (far below the surface of the Earth) become unstable when they are exposed at the surface or placed in contact with water, where the temperature and pressure are considerably lower. Unstable minerals transition into more stable minerals, resulting in the breakup of rock.
In some areas chemical weathering dominates due to a humid climate. Slightly acidic rainwater helps to form carbonic acid, promoting the disintegration of certain types of rocks. Limestone and marble may be chemically broken down as carbonic acid reacts with their carbonate mineral composition, forming cavities and caverns. Other Sedimentary rocks held together by carbonate cement are also particularly susceptible to chemical weathering, which expedites the process of soil formation.
The specific rock type at the surface has an important influence on the topography of a region. Certain rocks are able to resist weathering and erosion more easily than are others; resistant rocks that overlie weaker layers act as caps and form ridges. The shallow inland seas that advanced across the face of the continent during the Paleozoic preserved sediments that became the sedimentary rocks seen today throughout the Inland Basin and Blue Ridge.
Sedimentary rocks weather and erode differently than do crystalline (and generally harder) igneous and metamorphic rocks. Silica-rich igneous rocks have a crystalline nature and mineral composition that resists weathering far better than do the cemented grains of a sedimentary rock. The metamorphic equivalents of sedimentary and igneous rocks are often even more resistant due to recrystallization. There are exceptions, however, such as schist, which is much weaker than its premetamorphic limestone or sandstone state.
Erosion and deposition
Weathering causes a sediment particle—perhaps a single mineral grain—to be removed from its parent rock. Erosion has to do with the movement of these sediment particles from one place to another by the power of water or wind. Sometimes sediments move only a short distance, while other times they are moved great distances. Deposition occurs when a sediment particle reaches its final resting place (at least for a while!).
Topography and rock structure
The underlying structure of rock layers also plays an important role in surface topography. Sedimentary rocks are originally deposited in flat-lying layers that rest on top of one another. The movement of tectonic plates creates stress and tension within the crust, especially at plate boundaries. Intrusions beneath the surface may also cause deformation of the crust. All these different sources of geological stress can deform the flat sediment layers through folding, faulting, or overturning. These terms are collectively used to describe rock structure, and they can also be used to determine which forces have affected rocks in the past.
The folding of horizontal rock beds followed by erosion and uplift brings layers of rock to the surface. Tilted rocks expose underlying layers. Faulting likewise exposes layers at the surface to erosion, due to the movement and tilting of blocks of crust along the fault plane. For example, by the end of the Paleozoic, multiple phases of mountain building had produced the extensive Appalachian Mountain range, surrounded by folded and faulted strata that were deformed and wrinkled. For the last 200 million years, weathering has been dismantling the Appalachians and redistributing these sediments into extensive clastic wedges that form the wide Coastal Plain region. These sediment wedges are often over 15,000 meters (49,000 feet) thick and extend below current sea level to form the continental shelves. Above sea level, erosion continues to redistribute these sediments in multiple phases of fluvial erosion and deposition, ultimately depositing them along the coast to form barrier island complexes before ultimately transporting the sediment for final burial offshore; at least until the next tectonic phase of mountain building kick-starts the process all over again.
Just as we are able to make sense of the type of rocks in an area by knowing its geologic history, we are able to make sense of its topography based on rocks and structures resulting from past geologic events.
Summary
Topography is a central element of the broader concepts of geomorphology or physiography, which also include consideration of the shape (not just the height) of landforms, as well as the bedrock, soil, water, vegetation, and climate of an area, and how they interacted in the past to form the landscape we see today. A physiographic province is an area in which these features are similar, in which these features are significantly different from those found in adjacent regions, and/or is an area that is separated from adjacent regions by major geological features.
Regional guides to topography
Explore the topography of different regions of the United States:
- Northeastern U.S.: Central Lowland, Inland Basin, Appalachians and Piedmont, Coastal Plain, Exotic Terrane
- Midwestern U.S.: Central Lowland, Inland Basin, Superior Upland.
- Northwest-Central U.S.: Basin and Range, Central Lowland, Columbia Plateau, Great Plains, Rocky Mountains.
- Southeastern U.S.: Blue Ridge and Piedmont; Inland Basin; Coastal Plain.
- South-Central U.S.: Central Lowland, Interior Highlands, Coastal Plain, Great Plains, Basin and Range.
- Southwestern U.S.: Colorado Plateau, Basin and Range, Rocky Mountains, Great Plains.
- Western U.S.: Basin and Range, Columbia Plateau, Rocky Mountains, Cascade-Sierra Mountains, Pacific Border, Alaska.
- Hawai'i.
Topographic and geologic maps of the United States are also available here.



